Aug 28, 2016 Right-click on it New DWORD Value. Type TcpAutotuning and give it a vale of 1. Click OK and exit. To disable Receive Window Auto-Tuning feature for. I'm working on linux (2.6.43.8-1.fc15.i686.PAE) and face some problem to disable auto tuning of the TCP receiver window. I'm trying to find a given setting that would force my client to advertise a fixed receiver window. Mar 29, 2010 How to Enable or Disable Start Menu Auto Arrange by Name in Vista and Windows 7 This will show you how to enable or disable auto arrange to sort all programs menu by name or sort listed programs and program folder menus how you like in the Pin to and All Programs areas of the Start Menu. Oct 08, 2016 Bad Tweak – Disable Receive Window Auto-Tuning October 8, 2016, 11:11(EDT) By Eric (a.k.a. TweakHound) A reader just commented on this so this is a quickie article to debunk this “tweak”. Nov 24, 2015 Disabling auto-tuning, receive-side scaling, and heuristics almost eliminated the issue for me. If your environment consists of these particular operating systems, then you will want to disable auto-tuning, receive side scaling, and heuristics on both the workstations and servers.
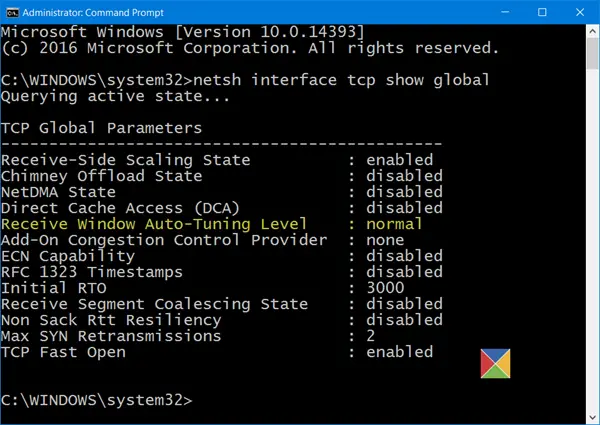
Open elevated command prompt with administrator’s privileges. Type the following command and press Enter: netsh interface tcp set global autotuning=normal.
-->Azure SQL Database is an automatically managed data service that constantly monitors your queries and identifies the action that you can perform to improve performance of your workload. You can review recommendations and manually apply them, or let Azure SQL Database automatically apply corrective actions - this is known as automatic tuning mode.
Automatic tuning can be enabled at the server or the database level through the Azure portal, REST API calls and T-SQL commands.
Note
For Managed Instance, the supported option FORCE_LAST_GOOD_PLAN can be configured through T-SQL only. Portal based configuration and automatic index tuning options described in this article do not apply to Managed Instance.
Note
Configuring Automatic tuning options through ARM (Azure Resource Manager) template is not supported at this time.
Enable automatic tuning on server
On the server level you can choose to inherit automatic tuning configuration from 'Azure Defaults' or not to inherit the configuration. Azure defaults are FORCE_LAST_GOOD_PLAN is enabled, CREATE_INDEX is enabled, and DROP_INDEX is disabled.
Important
As of March, 2020 changes to Azure defaults for automatic tuning will take effect as follows:
- New Azure defaults will be FORCE_LAST_GOOD_PLAN = enabled, CREATE_INDEX = disabled, and DROP_INDEX = disabled.
- Existing servers with no automatic tuning preferences configured will be automatically configured to INHERIT the new Azure defaults. This applies to all customers currently having server settings for automatic tuning in an undefined state.
- New servers created will automatically be configured to INHERIT the new Azure defaults (unlike earlier when automatic tuning configuration was in an undefined state upon new server creation).
Azure portal
Windows 10 Disable Auto Tuning
To enable automatic tuning on Azure SQL Database logical server, navigate to the server in Azure portal and then select Automatic tuning in the menu.
Note
Please note that DROP_INDEX option at this time is not compatible with applications using partition switching and index hints and should not be enabled in these cases. Dropping unused indexes is not supported for Premium and Business Critical service tiers.
Select the automatic tuning options you want to enable and select Apply.
Automatic tuning options on a server are applied to all databases on this server. By default, all databases inherit configuration from their parent server, but this can be overridden and specified for each database individually.
REST API
Find out more about using REST API to enable Automatic tuning on a server, see SQL Server Automatic tuning UPDATE and GET HTTP methods.
Enable automatic tuning on an individual database
The Azure SQL Database enables you to individually specify the automatic tuning configuration for each database. On the database level you can choose to inherit automatic tuning configuration from the parent server, 'Azure Defaults' or not to inherit the configuration. Azure Defaults are set to FORCE_LAST_GOOD_PLAN is enabled, CREATE_INDEX is enabled, and DROP_INDEX is disabled.
Tip
The general recommendation is to manage the automatic tuning configuration at server level so the same configuration settings can be applied on every database automatically. Configure automatic tuning on an individual database only if you need that database to have different settings than others inheriting settings from the same server.
Azure portal
To enable automatic tuning on a single database, navigate to the database in Azure portal and select Automatic tuning.
Individual automatic tuning settings can be separately configured for each database. You can manually configure an individual automatic tuning option, or specify that an option inherits its settings from the server.
Please note that DROP_INDEX option at this time is not compatible with applications using partition switching and index hints and should not be enabled in these cases.

Once you have selected your desired configuration, click Apply.
Rest API
Find out more about using REST API to enable Automatic tuning on a single database, see SQL Database Automatic tuning UPDATE and GET HTTP methods.
T-SQL
To enable automatic tuning on a single database via T-SQL, connect to the database and execute the following query:
How To Disable Automatic Updates Windows 10
Setting automatic tuning to AUTO will apply Azure Defaults. Setting it to INHERIT, automatic tuning configuration will be inherited from the parent server. Choosing CUSTOM, you will need to manually configure automatic tuning.
To configure individual automatic tuning options via T-SQL, connect to the database and execute the query such as this one:
Setting the individual tuning option to ON, will override any setting that database inherited and enable the tuning option. Setting it to OFF, will also override any setting that database inherited and disable the tuning option. Automatic tuning option, for which DEFAULT is specified, will inherit the automatic tuning configuration from the server level settings.
Important
In case of active geo-replication, Automatic tuning needs to be configured on the primary database only. Automatically applied tuning actions, such are for example index create or delete will be automatically replicated to the read-only secondary. Attempting to enable Automatic tuning via T-SQL on the read-only secondary will result in a failure as having a different tuning configuration on the read-only secondary is unsupported.
Find our more abut T-SQL options to configure Automatic tuning, see ALTER DATABASE SET Options (Transact-SQL) for SQL Database server.
Disabled by the system
Automatic tuning is monitoring all the actions it takes on the database and in some cases it can determine that automatic tuning can't properly work on the database. In this situation, tuning option will be disabled by the system. In most cases this happens because Query Store is not enabled or it's in read-only state on a specific database.
Permissions
As automatic tuning is Azure feature, to use it you will need to use Azure's built-in RBAC roles. Using SQL Authentication only will not be sufficient to use the feature from Azure portal.
To use automatic tuning, the minimum required permission to grant to the user is Azure's built-in SQL DB contributor role. You can also consider using higher privilege roles such are SQL Server Contributor, Contributor and Owner.
Disable Receive Window Auto Tuning
Configure automatic tuning e-mail notifications
See automatic tuning e-mail notifications guide.
Next steps
- Read the Automatic tuning article to learn more about automatic tuning and how it can help you improve your performance.
- See Performance recommendations for an overview of Azure SQL Database performance recommendations.
- See Query Performance Insights to learn about viewing the performance impact of your top queries.
I am uncertain about the more modern Windows OS like 8.1 and Server 2012. However, auto-tuning did not work correctly in Windows 7 and Server 2008 R2. One of the biggest symptoms was that GUI-based copy/paste between Windows 7 workstations and Server 2008 R2 servers would fail or creep along very slowly (think of copying a file to the company share or your home drive). Disabling auto-tuning, receive-side scaling, and heuristics almost eliminated the issue for me. If your environment consists of these particular operating systems, then you will want to disable auto-tuning, receive side scaling, and heuristics on both the workstations and servers. There is a hotfix but it may be just as easy to either script it or do it manually.
It is an easy fix and won't interrupt production.
EDIT: Has to be done with elevated privileges.